Deep Learning using Numpy
22 Jan 2017DeepLearning is a verstaile tool to solve problems that cannot be solved using traditional programming approach. I am a CTO at Datalog.ai where we solve lot of cool problems using Deep Learning. ML Researchers and Engineers use lot of Deep Learning packages like Theano, Tensorflow, Torch, Keras etc. Packages are really good but when you want to get an understanding on how Deep Learning works, it is better to go back to basics and understand how it is done. This blog is at an attempt at that, it is going to be a 3 part of series with topics being
- DeepLearning using Numpy
- Why TensorFlow/Theano not Numpy?
- Why Keras not TensorFlow/Theano?
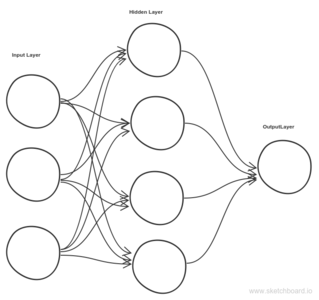
Deep learning refers to artificial neural networks that are composed of many layers like the one shown above. Deep Learning has many flavor’s like Convolution Neural Networks, Recurrent Neural Networks, Reinforcement Learning, Feed Forward Neural Network etc. This blog is going to take the simplest of them, Feed Forward Neural network as an example to explain.
Machine Learning deals with lot of Linear Algebra operations like dot product, transpose, reshape etc. If you are not familiar with it, I would suggest refer to my previous blog post in All about Math section.
Deep Learning needs an activation function to squish real numbers to probability values between 0 and 1 , there are different activation functions like sigmoid, Tanh, RELU etc. For this toy example i have used sigmoid activation function.
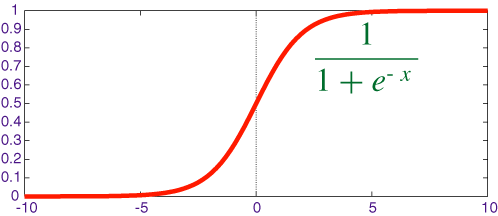
We are going to use Gradient Descent to find optimal parameters to solve for Y. Gradient descent uses the derivative of the sum of errors to update the systems parameters a little bit in such a way that the error decreases as much as possible.After every update the system learns to predict with a lower error. Let it run many iterations and it will converge at some optima(local). Sigmoid function takes a parameter to calculate Derivative. Don’t worry if you don’t understand this explanation, it is very intuitive if you can follow the code along. If you are looking for more explanation refer to this video by Prof Andrew Ng.
For this example on Numpy Deep Learning Code, I am going to use a synthetic dataset. Output is the target we are going to predict.
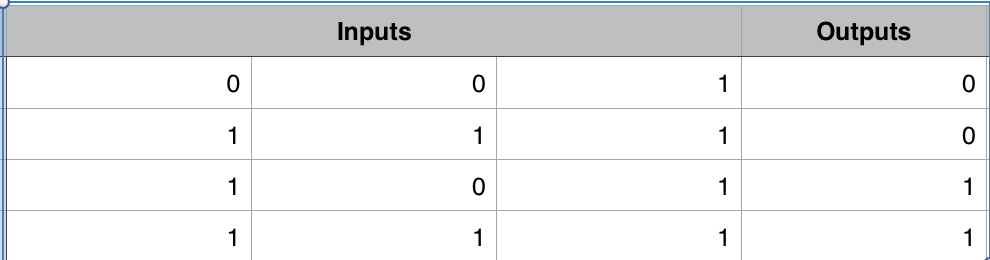
Randomly initialize weights for 2 synapses. Synapses 0 will be of shape 3x4, Synapses 1 will be of shape 4x1
With Gradient descent you have to run the process for n number of iterations, in ML lingo it is called epoch (since it will take ages to complete). In our case we are going to run it for 50 iterations. Since this is a 1 hidden Layer network, we do a dot product between input l0 and synapses_0 and then squish it using sigmoid function. Pass output of l1 as input to hidden layer and do dot product between l1 and synapses_1 weights and then squish it using sigmoid function.
Now we are off to calculate what is the error for our prediction for l2 layer. Then use derivative to find out how much we should update our Synapses 1.
Same step should be done for l1 layer, but error should be calculated based on how much we are off on l2.
Update weights for synapses_0 and synapses_1 based on calculated l1_delta and l2_delta respectively.
See below on how loss is decreasing for each iteration.
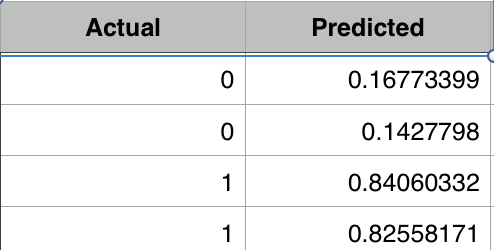
With just 50 iterations we are very close to actual value
Siraj Raval has a really good youtube video on Intro to Deep Learning check it out too.